Add Services to the VotingApp
-
In the votingapp directory, create YAML files containing the specifications for the Services of each microservice in the application, according to the table below:
Microservice File Name Service Type Service Details Vote UI svc-voteui.yaml NodePort (31000) nodePort 31000, port: 80, targetPort: 80 Vote svc-vote.yaml ClusterIP port: 5000, targetPort: 5000 Redis svc-redis.yaml ClusterIP port: 6379, targetPort: 6379 Postgres svc-db.yaml ClusterIP port: 5432, targetPort: 5432 Result svc-result.yaml ClusterIP port: 5000, targetPort: 5000 Result UI svc-resultui.yaml NodePort (31001) nodePort 31001, port: 80, targetPort: 80 Note that it is not necessary to expose the worker Pod with a Service as no Pod needs to connect to it. Instead, it is the worker Pod that connects to redis and db.
For each Pod/Service pair, make sure to properly define a label in the Pod and the corresponding selector in the Service.
-
Deploy the application defined by these specifications
-
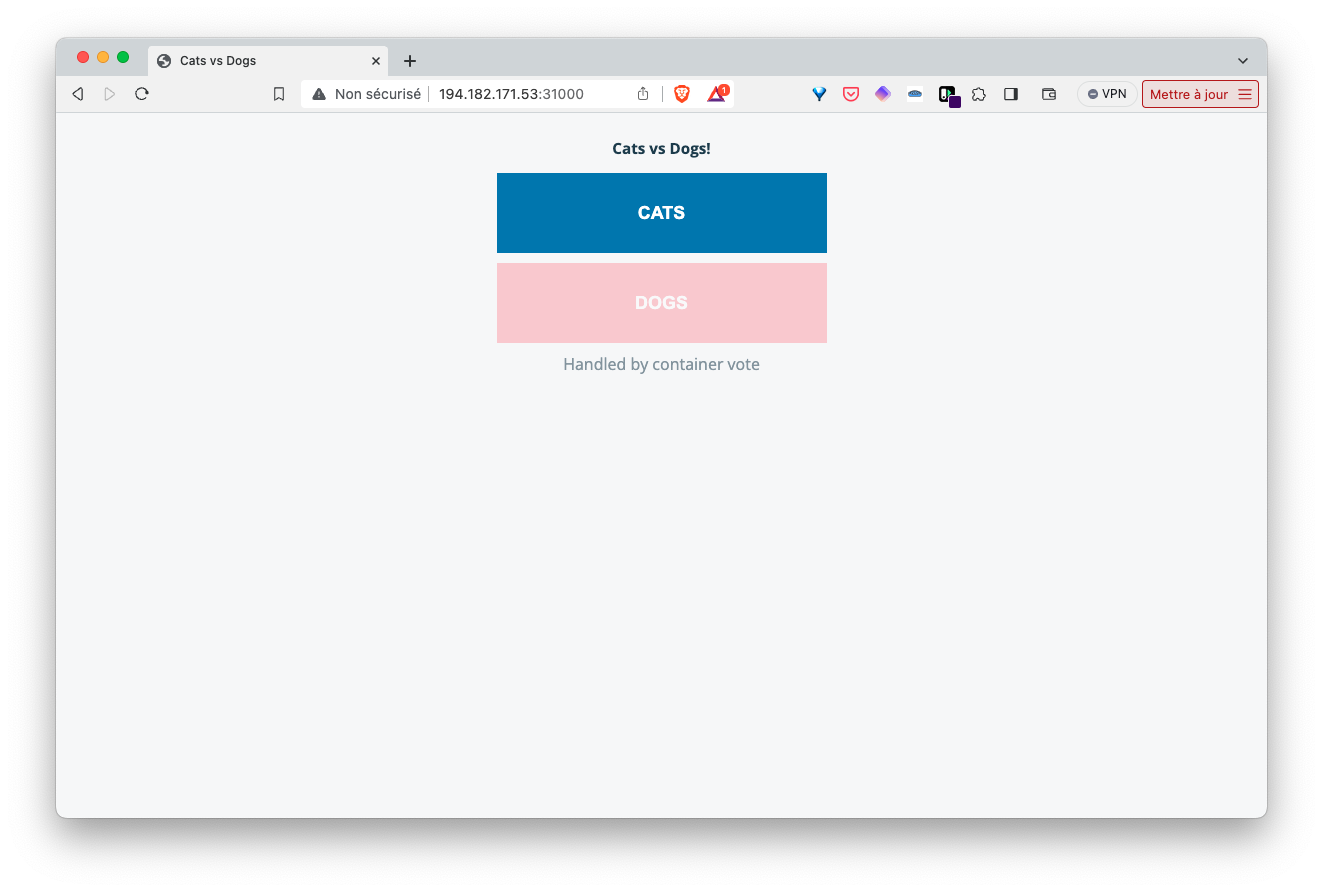
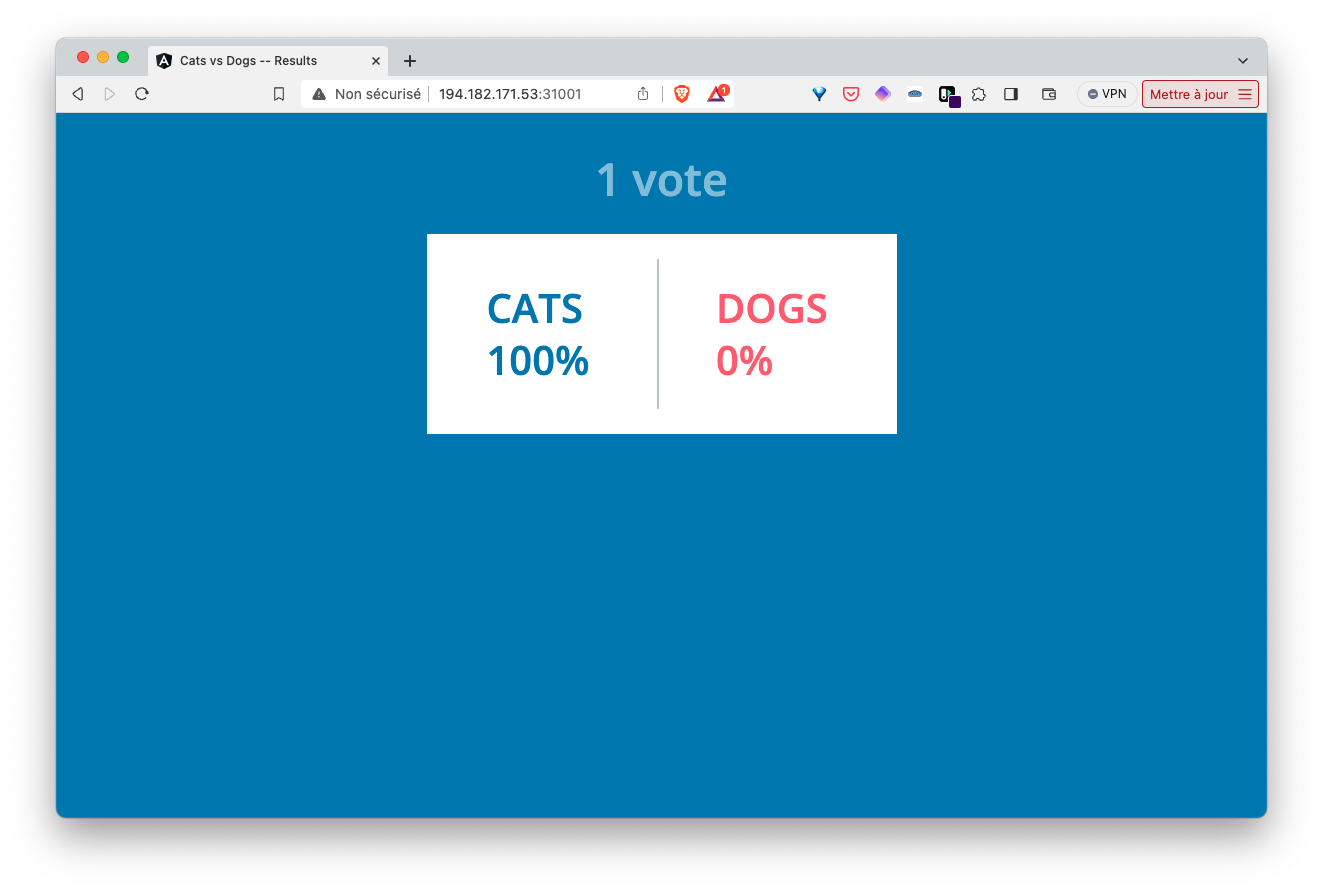
Access the vote and result interfaces via the NodePort Services
-
Delete the application
Solution
- The Service specifications are as follows:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: vote-ui
name: vote-ui
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
nodePort: 31000
selector:
app: vote-uiapiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: vote
name: vote
spec:
ports:
- port: 5000
targetPort: 5000
selector:
app: voteapiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: redis
name: redis
spec:
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- port: 6379
targetPort: 6379
selector:
app: redisapiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: db
name: db
spec:
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- port: 5432
targetPort: 5432
selector:
app: dbapiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: result
name: result
spec:
ports:
- port: 5000
targetPort: 5000
selector:
app: resultapiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: result-ui
name: result-ui
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
nodePort: 31001
selector:
app: result-ui- Deploy the application with the following command from the votingapp directory:
kubectl apply -f .- The different Pods are now in Running status:
$ kubectl get po,svc
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/db 1/1 Running 0 20s
pod/redis 1/1 Running 0 20s
pod/result 1/1 Running 0 20s
pod/result-ui 1/1 Running 0 20s
pod/vote 1/1 Running 0 20s
pod/vote-ui 1/1 Running 0 21s
pod/worker 1/1 Running 0 20s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/db ClusterIP 10.100.10.36 <none> 5432/TCP 20s
service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 29m
service/redis ClusterIP 10.107.167.249 <none> 6379/TCP 20s
service/result ClusterIP 10.105.157.142 <none> 5000/TCP 20s
service/result-ui NodePort 10.101.30.191 <none> 80:31001/TCP 20s
service/vote ClusterIP 10.96.108.192 <none> 5000/TCP 20s
service/vote-ui NodePort 10.104.203.9 <none> 80:31000/TCP 20sUsing the IP address of one of the cluster nodes, we can access the vote and result interfaces via ports 31000 and 31001 respectively.
- Delete the application with the following command:
kubectl delete -f .